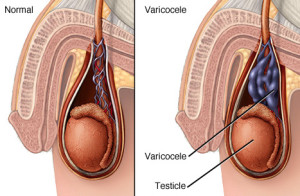
 Similar to varicose veins in the leg, varicoceles are a network of abnormally enlarged veins that drain blood from the testicles. They usually develop in the scrotum on the left side during or after puberty. Although most cases of varicoceles appear in the left side, they can affect sperm production in both testicles.
Similar to varicose veins in the leg, varicoceles are a network of abnormally enlarged veins that drain blood from the testicles. They usually develop in the scrotum on the left side during or after puberty. Although most cases of varicoceles appear in the left side, they can affect sperm production in both testicles.
Varicoceles do not resolve on their own once they develop. Many patients do not experience any symptoms from varicoceles, but when present symptoms can include:
- Varying degrees of pain, especially during certain movements
- Swelling in the scrotum
- Testicular atrophy
- Abnormal or insufficient sperm production
- Slower or limited growth in affected testicle
- Infertility
What Causes Varicoceles?
The exact cause of varicoceles is not clear, but a potential cause is believed to be a malfunction in the valves of the scrotal veins, causing irregular blood flow that pools and causes the veins to dilate (become enlarged). Some experts also speculate that the positioning of the vein leading from the left kidney to the scrotum allows for stronger gravitational pull than on the right side.
When to See a Urologist for Treatment
Many men suffering from varicoceles do not experience symptoms, and as such are unaware of their condition. In the absence of symptoms, they are typically discovered during routine physical examinations. However patients should seek medical attention in cases where pain persists, the testicles appear to be significantly different in size, there is a mass, or if experiencing problems with fertility.
Varicocelectomy
 What is a Varicocelectomy?
What is a Varicocelectomy?
Varicocelectomy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to provide relief for men suffering from a urological condition known as varicoceles. The surgeon will make a small incision in the groin and, using a microscope to assist in visualization, cut the veins responsible for the irregular blood flow and pooling that causes the varicoceles. Varicocelectomy is a minimally invasive procedure, and patients can typically go home the same day of the procedure.
Recovery from a varicocelectomy typically involves avoiding strenuous physical activity for several weeks after the procedure. Pain medication is provided to patients, but typically discomfort is minimal after the procedure.
Candidates for Varicocelectomy
After a comprehensive medical history, physical exam and semen analysis (if necessary), a urologist will help determine whether a varicocelectomy is the best course of action.
Varicocele Experts
A varicocele is an enlarged vein in the scrotum, with irregular blood flow and pooling of blood in the vein. A definitive cause for varicoceles is unclear, but the anatomy of the male reproductive system, specifically the vein’s proximity to the left kidney, could potentially cause a stronger gravitational pull that increases the likelihood of developing a varicocele. (The majority of varicoceles occur in the left testicle).
In many cases varicoceles do not produce symptoms, and may not require treatment. Varicoceles can potentially lead to abnormalities with sperm production, and ultimately infertility in men. For patients that do experience symptoms, the most common are pain, swelling, and shrinkage of the testicles. While the most common location of a varicocele is on the left, it can affect sperm production in both testicles. A board certified urologist and varicocele expert at Comprehensive Urology in Beverly Hills can typically diagnose a varicocele in asymptomatic patients through a routine physical examination.
Although many cases of varicoceles do not present symptoms, patients should seek help and treatment from a varicocele expert at Comprehensive Urology if experiencing any of the following symptoms:
- Pain
- Swelling
- A testicle that appears smaller than the other
- Problems with fertility
Varicoceles usually occur at some point around the onset of puberty, and are most common on the left. However sperm quality and production can be affected on both sides, regardless of the location of the varicocele. When treatment is required, an experienced urologist will perform a procedure known as a varicocelectomy to repair the enlarged scrotal vein. Varicocelectomies are minimally invasive, out patient procedures where the patient can typically go home on the same day. Recovery involves rest and abstaining from physical exertion for a short period after the procedure, and medication for soreness or pain management if necessary.
Varicocele Embolization
 Varicocele embolization, also known as catheter-directed embolization, is a nonsurgical treatment for symptomatic varicoceles. A varicocele is an enlarged varicose vein of the testicle and scrotum that may cause pain and lead to testicular atrophy (shrinkage of the testicles). It may also lead to infertility if left untreated. Varicocele embolization involves using a catheter to place a tiny coil and/or embolic fluid in the dysfunctional vein to shut off blood flow, which will allow the patient to be relaxed and relieved from pain. It is a safe procedure that has helped improve sperm quality of infertile men.
Varicocele embolization, also known as catheter-directed embolization, is a nonsurgical treatment for symptomatic varicoceles. A varicocele is an enlarged varicose vein of the testicle and scrotum that may cause pain and lead to testicular atrophy (shrinkage of the testicles). It may also lead to infertility if left untreated. Varicocele embolization involves using a catheter to place a tiny coil and/or embolic fluid in the dysfunctional vein to shut off blood flow, which will allow the patient to be relaxed and relieved from pain. It is a safe procedure that has helped improve sperm quality of infertile men.
How to Prepare for Varicocele Embolization
While medical professionals will ensure that your procedure is performed correctly, preparation by patients can help ensure that a varicocele embolization will have the best chance at success as possible. Preparations that patients can take include:
- Report all medications you are taking to your doctor, including herbal medications.
- Report all known allergies to medications, including local anesthetic medications, general anesthesia, or to contrast materials containing iodine.
- Your doctor may advise you to stop taking aspirin, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or blood thinners for a specified period of time before your procedure.
- Follow specific instructions from your doctor, including any schedule changes in your medication intake.
- For those who will be sedated during the procedure, you may be required to not eat or drink anything for four to eight hours prior to surgery.
How is the Embolization Procedure Performed?
Varicocele embolization is an image-guided, minimally invasive procedure that can be performed by a urologist or interventional radiologist. Embolization does not require any stitches or general anesthesia, although sedation and local anesthesia may be given as needed.
The procedure involves making a minor incision, about ¼ of an inch, and inserting a small catheter into a leg vein or neck vein through the incision. This tube is then placed into the varicocele vein under X-ray guidance. Small amounts of X-ray dye (contrast) are injected to ensure the position of the catheter for precise placement. This is followed by inserting a tiny coil in the vein to block the flow of blood, or pressure in the varicocele. Blood can still exit the testicle through other normal pathways. Once the flow of blood in the affected vein has stopped completely, the catheter can be removed. Generally, the procedure is completed in in hour and patients may return to normal activities within two to three days after the procedure.
What are the Benefits of Varicocele Embolization?
This procedure is a minimally invasive approach to varicocele treatment that requires no surgical incisions. A tiny incision in the skin, about ¼ of an inch, is made in order to insert the instrument. However, the nick in the skin is so minor it does not require any stitches to close. The recovery time with embolization is significantly shorter than with surgery. Additionally, there is a 90% success rate with embolization, which is comparable to the effectiveness of more invasive surgical methods for treating the same condition.
What are the Risks Associated with Varicocele Embolization?
As with any procedure that involves penetrating the skin, the risk of infection is something to consider. However, the chances of acquiring a serious infection that will need antibiotic treatment appear to be less than one in 1,000. Another minor risk associated with embolization is having an allergic reaction once the contrast material is injected. Placement of a catheter inside a blood vessel also carries the risk of damaging the blood vessel, along with bruising or bleeding at the site of placement and infection. In some cases, an embolic agent may be lodged in the wrong place, which will deprive the normal tissue of its oxygen supply. Other possible side effects to consider are cancer from radiation exposure, lower back pain, inflammation within the scrotum and phlebitis.
Robotic Varicocelectomy
Coming Soon!
Microsurgery for Varicocele
A varicocele is a condition where a series of testicular veins are overly enlarged. Varicoceles have been associated with low sperm production and decreased sperm quality, which can often lead to infertility. This condition can also cause the testicles to shrink or hinder its normal development.
Varicocele and Male Infertility
 The presence of a varicocele may result in infertility. If diagnosed in a timely fashion, treatment options are available to treat varicoceles and to improve male fertility. The microsurgical treatment for varicoceles (microsurgical varicocelectomy procedure) is a highly precise and effective approach for the treatment of varicoceles and varicocele induced infertility. Microsurgical varicocelectomy can lead to improved sperm counts and improved sperm quality in men with varicocele induced infertility.
The presence of a varicocele may result in infertility. If diagnosed in a timely fashion, treatment options are available to treat varicoceles and to improve male fertility. The microsurgical treatment for varicoceles (microsurgical varicocelectomy procedure) is a highly precise and effective approach for the treatment of varicoceles and varicocele induced infertility. Microsurgical varicocelectomy can lead to improved sperm counts and improved sperm quality in men with varicocele induced infertility.
The exact cause of infertility in men with varicoceles is not clearly understood, however, most medical professionals and research suggest that these symptomatic veins interfere with the normal heat exchange mechanism in the testicles. When the veins are enlarged because of high pressure in the veins or poorly functioning valves, intratesticular temperatures are elevated, impairing their ability to make sperm.
Microsurgery Treatment
Surgical treatment of varicocele aims to block the flow of blood into the affected vein in order to redirect the flow to other, normal veins in the testicles. Although treatment is not always needed, indications that you may need to repair a varicocele include progressive testicular atrophy (the testicle becomes smaller), testicular pain or abnormal semen analysis results. The risks associated with varicocele repair, although rare, may include:
- Infection
- Damage to an artery
- Hydrocele, which is the buildup of fluid around the testicles
- Recurrence of varicoceles
- Testicular atrophy
Microsurgical varicocele utilizes magnification of the operative field through the use of an operating microscope. This coupled with the use of microsurgical instruments, leads to lower complication rates and better outcomes. The surgical reparation of the varicocele involves making a small incision in the groin area. The surgeon will utilize a microscope to locate the veins leading to the varicocele and cuts off the flow of blood to these abnormally enlarged veins by using microsurgical clips or sutures. The incision will be closed with a few minor sutures.
Surgery Preparation
Generally, patients are advised not to take aspirin for about one week prior to surgery. You will also be advised to not eat or drink anything eight hours prior to your scheduled surgery, including water.
What to Expect After Surgery
Immediately after the procedure, you should expect to feel groggy. It is best to arrange for someone to pick you up and take you home directly from the hospital. Your doctor may prescribe you pain medication and antibiotics.
Most patients will be able to return to work or normal, non-strenuous activities (such as bathing) after 48 hours of full recovery. One week must pass before resuming to sexual activity, or whenever you feel comfortable to do so. The quality of sperm should improve about three to six months after the surgical procedure.
Varicocele Treatment with an Expert Urologist
As with any medical procedure, there are benefits and risks to treating a specific condition. Choosing the right medical expert to treat your condition is crucial to achieving the best possible outcomes. At Comprehensive Urology, our skilled, board-certified urologists have years of experience performing varicocele embolization along with other urological procedures. If you would like to learn more about your options, please call (310) 499-2756 to schedule an initial consultation at our Los Angeles office.
Next, read about Erectile Dysfunction.